The calculator can be used to solve for s u a or t. Enter 180 in the velocity box and choose miles per hour from its menu.
Acceleration Examples Solutions Videos Notes
The distance covered is articulated by.

Distance velocity acceleration formula. V is final velocity in ms. Velocity is speed in a given direction. Final velocity 2 initial velocity 2 2 acceleration distance.
In other words the total distance traveled is 402 meters or a quarter mile. Click CALCULATE and your answer is 25 miles or 13200 feet or 158400 inchesetc Heres hoping this calculator helps you with those math problems. Velocity equals distance traveled divided by time of travel the speed plus the direction of travel.
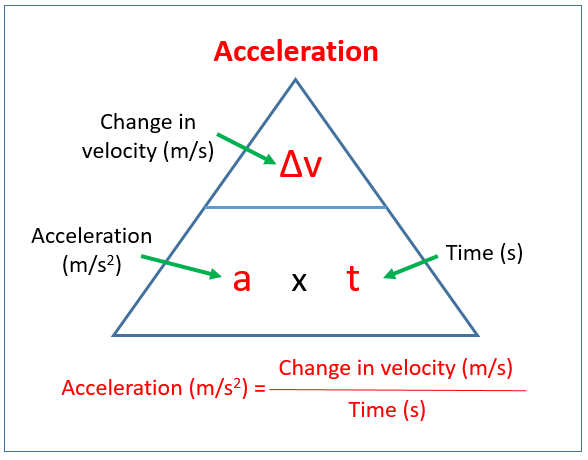
It is manipulated below to show how to solve for each individual variable. Acceleration is change in velocity divided by time. Initial velocity u 0 ms because it was at rest - not moving change in velocity v 28 - 0 28 ms.
This tells you how to find acceleration with velocity and distance. D 1640 m The stopping distance of the car is 1640 m. Therefore if you divide speed by time as we do in the first acceleration formula youll get acceleration unit fts² or ms² depending on which system you use.
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus says that. This gives you the distance traveled during a certain amount of time. D vt 12at2 where d is distance traveled in a certain amount of time t v is starting velocity a is acceleration must be constant and t is time.
2 A driver in a car on an icy highway is traveling at 1000 kmh. Using the integral calculus we can calculate the velocity function from the acceleration function and the position function from the velocity function. T is time in s.
1 to va 333 ms - 0 ms 2 167 ms. V2-u22as v2 u2 2as. You still need the distance and you can get it this way.
If Fu is an anti-derivative of fu then b afudu Fb Fa. Velocity acceleration and distance This equation applies to objects in uniform acceleration. The indefinite integral is commonly applied in problems involving distance velocity and acceleration each of which is a function of time.
In the discussion of the applications of the derivative note that the derivative of a distance function represents instantaneous velocity and that the derivative of the velocity function represents instantaneous acceleration at a particular time. We think of a as a fixed starting value x0. Enter 50 in the time box and choose seconds from its menu.
Suppose that we want to let the upper limit of integration vary ie we replace b by some variable x. The average velocity can be calculated with eq. Because vf vi at you know that.
The basic equation for solving this is. The equation used is s ut ½at 2. Now you have the time.
Velocity is a vector value meaning that velocity includes direction. At dv dt d2x dt2. Alternatively you can use the third equation.
Divide both sides by 2 s and reverse the equation to get. Initial Velocity u 0 because the stone was at rest t 4s t is Time taken a g 98 ms 2 a is Acceleration due to gravity distance traveled by stone Height of bridge s. S 0 12 98 4 196 ms 2.
T2 t1 atdt vtt2 t1 vt2 vt1. Calculator Use This Displacement Calculator finds the distance traveled or displacement s of an object using its initial velocity u acceleration a and time t traveled. Average speed is distance divided by time.
If this distance is so small that omitting segment four would not suffice then segments two and six constant acceleration could be equally reduced and the constant velocity limit would not be reached. A is acceleration in mss or ms 2. Afrac v2-u2 2s a 2sv2u2.
Segment fours time period constant velocity varies with distance between the two positions. The equation for acceleration can also be represented as. Movement can be shown in distance-time and velocity-time graphs.
A motorcycle starts with an initial velocity 0 kmh 0 ms and accelerates to 120 kmh 333 ms in 5 s. And the acceleration is given by. Therefore s 196 ms 2.
Calculate the average acceleration of the car. A v-u div t where. For example the velocity of a train traveling 1500 kilometers eastward from San Francisco in 12 hours would be 1500 km divided by 12 hr east or 125 kph east.
U is initial velocity in ms. Must be a quarter-mile racetrack. A v 2 u 2 2 s.
Remember though that this only applies to constant acceleration in one direction. We next recall a general principle that will later be applied to distance-velocity-acceleration problems among other things. The stopping distance can be found using the formula.
V 2 u 2 2 a s. Final velocity v 28 ms. The second term drops out because vi 0 so all you have to do is plug in the numbers.
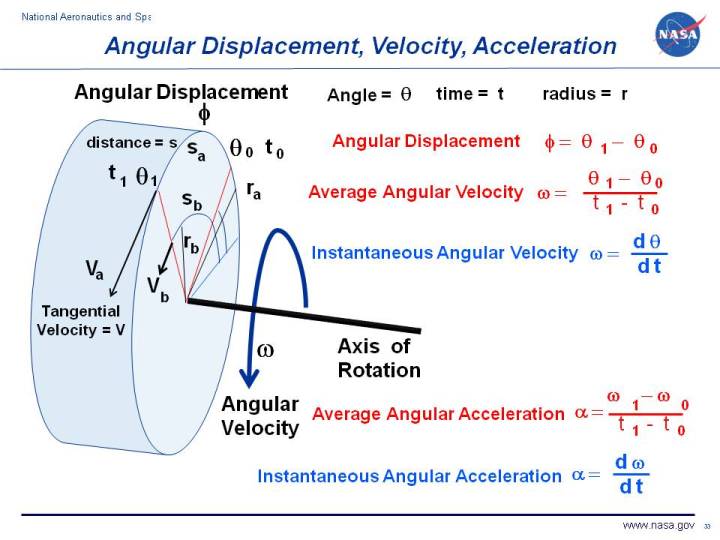
Angular Displacement Velocity Acceleration
Malaysia Pmr Spm Student S Learning Portal Provides Free Notes E Books References Formula List For Teachers Students For Tuition Or School Study Purposes
