099 FDISTA2A3A4FALSE F probability using the probability density function FALSE cumulative argument. Find a z c value from a confidence level c.
/confidencet-56fb46a45f9b58298681430e.jpg)
Functions With The T Distribution In Excel
If you want something that is mathematically rigorous please look elsew.
Degrees of freedom excel. Can also be used for n ³ 30. T c TINV1-cdf Calculate an error tolerance E of a mean for n ³ 30 using sx. DF_POOLEDR1 R2 degrees of freedom for the two-sample t-test with unequal variances for samples in ranges R1 and R2 ie.
In cell A17 type a label t-crit for the critical value. For a one sample T test DOF is the number of values in sequence 1 minus one. If tails 2 TDIST returns the two-tailed distribution.
Definition Formula Example Definition. ABS TINV 005 11 This returns the value 179588. Formula for Degrees of Freedom.
E t c sxSQRTn. A test used for comparison of two means is t-test in statistics. The number of values of a system that varies independently is called as degrees of freedom DOF.
In this video we define degrees of freedom and use a t-table to find a critical value. Z c ABSNORMSINV1-c2 Find a t c value from a confidence level c. This is an arm-waving proof.
The statistical formula to determine degrees of freedom is quite simple. The result is 2306. The number of degrees of freedom for the denominator is the total number of data values minus the number of groups or n - c.
TTESTR1 R2 tails type p-value of the t-test for the difference between the means of two samples R1 and R2 where tails 1 one-tailed or 2 two-tailed and type takes the values. The number of independent ways by which a dynamic system can move without violating any constraint imposed on it is called number of degrees of freedom. In this video we define degrees of freedom and use a t-table to find a critical value.
An introduction to the concept of degrees of freedom. The Real Statistics Resource Pack provides the following functions. This is the critical value for a two-tailed test with significance level of 005 and degrees of freedom 11.
The TDIST function requires a t-value the degrees of freedom and a 2 for a two-tailed test which is most often what you need. Type - 1 denotes a paired t-test 2 a two-sample test with the same population variance and 3 a two-sample test with different population variances. Degrees of freedom Now look at the DF values.
In statistics the number of degrees of freedom is the number of values in the final calculation of a statistic that are free to vary. Tails in which we can enter either 1 or 2. Array 1 which gives the first set of sample data.
It is clear to see that we must be very careful to know which inference procedure we are working with. In B17 type a formula to calculate the critical t value. The formula to find the degrees of freedom varies dependent on the type of test.
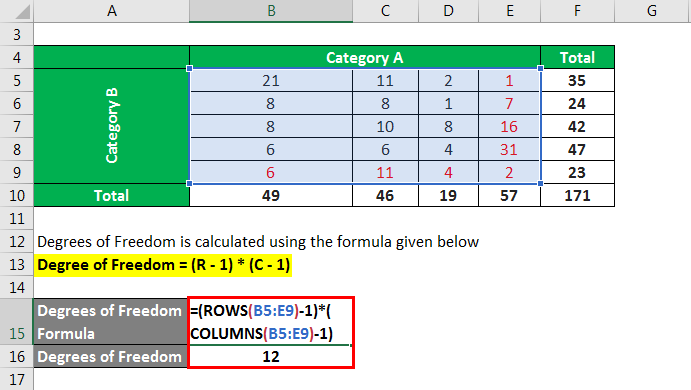
To find the T critical value for a right-tailed test with a significance level of 005 and degrees of freedom 11 we can type the following formula into Excel. Degrees of Freedom 5 1 4 1 Degrees of Freedom 12. The number of degrees of freedom for the numerator is one less than the number of groups or c - 1.
Via trial and error where I guess the number of statistical degrees of freedom I have determined that the single variable linear regression automatically performed by Excel provides a p-value for the Y-axis-intercept that is identical to the one that can be calculated by explicit Excel functions as follows. The degrees of freedom in a statistical calculation represent how many values involved in a calculation have. E z c sxSQRTn Calculate an error tolerance E of a mean for n 30 using sx.
Denominator degrees of freedom. This function returns the critical value from the F distribution based on the significance level numerator degrees of freedom and denominator degrees of freedom provided. Estimates of statistical parameters can b.
Numerator degrees of freedom. Array 2 which gives the second set of sample data. For example suppose we would like to find the F critical value for a significance level of 005 numerator degrees of freedom 4 and denominator degrees of freedom 6.
Result FDISTA2A3A4TRUE F probability using the cumulative distribution function TRUE cumulative argument. Excel provides the function TTEST to handle the various two-sample t-tests. M in Theorem 1.
The total DF bottom row is 17. In other words the number of degrees of freedom can be defined as the minimum number of independent coordinates that can specify the position of the system completely. If tails 1 TDIST returns the one-tailed distribution.
This is the total number of values 18 minus 1. 1 CHIDIST x df and CHISQDIST x df FALSE is the pdf for the chi-square distribution. In Excel 2010 CHISQDIST x df TRUE is the cumulative distribution function for the chi-square distribution with df degrees of freedom ie.
Deg_freedom required argument An integer that indicates the number of degrees of freedom. Tails required argument This specifies the number of distribution tails that would be returned.